HVAC & Refrigeration
HVAC & Refrigeration
The most distinctive in today modern HVAC is use the of energy efficiency system, this help reducing electricity bills while maintaining a comfortable environment. Inverter technology on variable speed drive compressor can adjust output dynamically, smart control integration with IoT enable remote control and monitoring via smart phones.
The use more environmentally friendly refrigerant such as R-410A and R32 can be alternative to ozone depleting. Advance filtration for higher requirement surpassing older system, HEPA filtration with UV-C and ionization technology to address allergens, pathogens and pollutants.
Improved materials and VSD reduce noise and space requirements, sensors equipment, improved ducting with minimal leakage make modern HVAC leverage its function beyond comfort.






Chiller & System
A variable speed drive (VSD) chiller compressor refers to a type of compressor used in chiller systems that can adjust its speed based on the cooling demand of the process it serves.
AHU Size and Capacity for Medium-scale typically range of 2,000 to 20,000 CFM (cubic feet per minute). Unit can be customized to suit specific applications, including rooftop, indoor, and outdoor installations
Filters medium or high-efficiency filters, including HEPA filters, to ensure excellent indoor air quality, mixing box and secondary filter section are optional features for enhanced air mixing and filtration capabilities
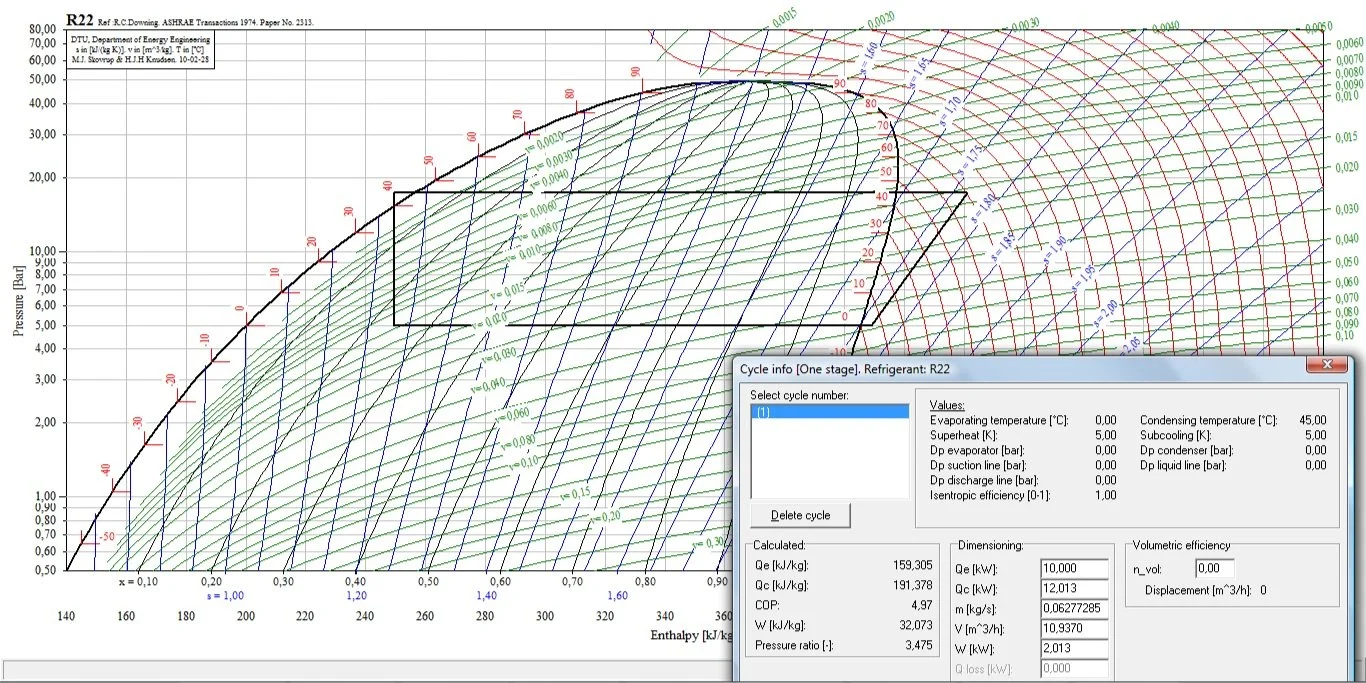
The refrigeration cycle is the backbone of HVAC systems, enabling cooling and heating by transferring heat from one area to another.
Compressor: Acts as the heart of the cycle, compressing the refrigerant gas to increase its pressure and temperature. The refrigerant gas is compressed, raising its pressure and temperature.
Condenser: Releases the heat absorbed by the refrigerant, cooling it down and converting it into a liquid. The high-pressures refrigerant releases heat and condenses into a liquid.
Expansion Valve: Reduces the pressure of the refrigerant, causing its temperature to drop. The liquid refrigerant passes through the expansion valve, dropping in pressure and temperature.
Evaporator: Absorbs heat from the indoor air, cooling the space as the refrigerant evaporates into a gas. The refrigerant absorbs heat from the indoor air, cooling the space as it evaporates back into a gas.
A psychrometric chart is a powerful tool used to visualize the properties of moist air and the relationships between its temperature, humidity, and energy content. It's essential for HVAC design, especially when dealing with air conditioning, heating, and ventilation systems.
Dry Bulb Temperature: Horizontal lines representing the regular air temperature.
Humidity Ratio: Vertical axis showing the amount of water vapor in the air.
Wet Bulb Temperature: Diagonal lines indicating cooling effect through evaporation.
Relative Humidity: Curved lines showing the percentage of moisture in the air.
Dew Point Temperature: A point where air becomes saturated and condensation begins.
Enthalpy: Lines showing the total heat energy in the air